Hibernate Tutorial for Senior Developers and Architects
Master Advanced ORM Concepts, Performance Optimization, and Enterprise Patterns
This comprehensive Hibernate tutorial is designed for senior developers and architects who need to understand advanced ORM concepts, performance optimization techniques, and enterprise-level patterns. We'll cover everything from basic mapping to complex caching strategies and distributed transaction management.
Table of Contents
1. Hibernate Fundamentals for Architects
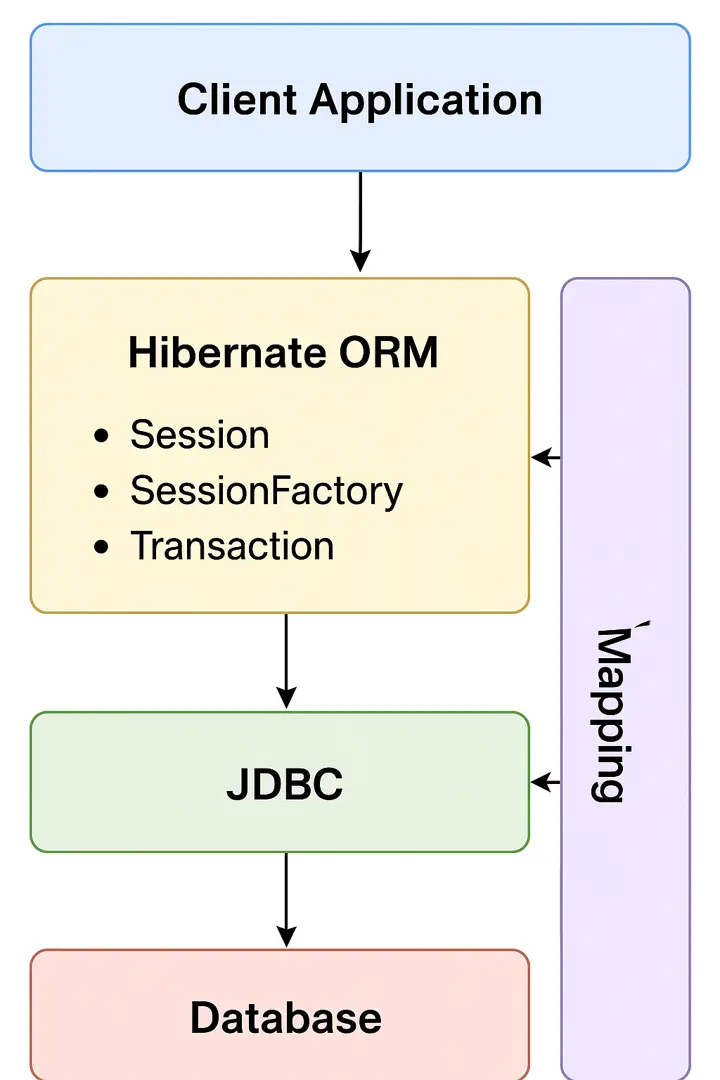
Understanding Hibernate's architecture is crucial for making informed decisions about ORM strategies in enterprise applications.
Core Architecture Components
- SessionFactory: Thread-safe factory for creating Session instances
- Session: Single-threaded, short-lived object representing a conversation with the database
- Transaction: Atomic unit of work with ACID properties
- ConnectionProvider: Manages database connections
- Dialect: Database-specific SQL generation
Configuration Strategies
Programmatic Configuration
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.connection.driver_class", "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.connection.url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/enterprise_db");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.connection.username", "app_user");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.connection.password", "secure_password");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "validate");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "false");
configuration.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql", "true");2. Advanced Mapping Strategies
Master complex entity relationships and mapping patterns used in enterprise applications.
Inheritance Mapping Strategies
- Table per Class Hierarchy: Single table with discriminator column
- Table per Subclass: Separate tables with foreign key relationships
- Table per Concrete Class: Independent tables for each concrete class
Collection Mapping Best Practices
Lazy Loading Configuration
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "order", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@LazyCollection(LazyCollectionOption.EXTRA)
private List<OrderItem> items = new ArrayList<>();3. Performance Optimization
Critical performance optimization techniques for high-traffic enterprise applications.
Query Optimization
- N+1 Problem Solutions: Batch fetching, join fetching, subselect fetching
- Pagination Strategies: Offset-based vs cursor-based pagination
- Bulk Operations: Batch inserts, updates, and deletes
Connection Pool Configuration
HikariCP Configuration
hibernate.hikari.maximumPoolSize=20
hibernate.hikari.minimumIdle=5
hibernate.hikari.idleTimeout=300000
hibernate.hikari.maxLifetime=1200000
hibernate.hikari.connectionTimeout=20000
hibernate.hikari.leakDetectionThreshold=600004. Caching Strategies
Implement effective caching strategies to improve application performance and reduce database load.
Cache Levels
- First Level Cache: Session-scoped cache (automatic)
- Second Level Cache: SessionFactory-scoped cache (configurable)
- Query Cache: Caches query results
Cache Providers
- EhCache: In-memory caching with disk overflow
- Redis: Distributed caching for clustered applications
- Hazelcast: In-memory data grid with clustering
- Caffeine: High-performance local cache
5. Transaction Management
Master transaction management patterns for enterprise applications with complex business logic.
Transaction Isolation Levels
- READ_UNCOMMITTED: Lowest isolation, highest performance
- READ_COMMITTED: Default for most databases
- REPEATABLE_READ: Prevents phantom reads
- SERIALIZABLE: Highest isolation, lowest performance
Distributed Transaction Patterns
Saga Pattern Implementation
@Transactional
public void processOrder(Order order) {
try {
// Step 1: Reserve inventory
inventoryService.reserveItems(order.getItems());
// Step 2: Process payment
paymentService.chargeCustomer(order.getCustomerId(), order.getTotal());
// Step 3: Create shipment
shippingService.createShipment(order);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Compensating transactions
compensateOrder(order);
throw e;
}
}6. Enterprise Patterns
Implement proven enterprise patterns for scalable and maintainable Hibernate applications.
Repository Pattern
Generic Repository Implementation
@Repository
public class GenericRepository<T, ID> {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public T save(T entity) {
if (entityManager.contains(entity)) {
return entityManager.merge(entity);
} else {
entityManager.persist(entity);
return entity;
}
}
public Optional<T> findById(ID id) {
return Optional.ofNullable(entityManager.find(getEntityClass(), id));
}
public List<T> findAll() {
CriteriaQuery<T> query = entityManager.getCriteriaBuilder()
.createQuery(getEntityClass());
return entityManager.createQuery(query).getResultList();
}
}Unit of Work Pattern
- Change Tracking: Automatic dirty checking
- Lazy Loading: Deferred object loading
- Identity Map: Single instance per identity
- Write-Behind: Deferred database writes
7. Monitoring & Troubleshooting
Essential monitoring and troubleshooting techniques for production Hibernate applications.
Performance Monitoring
- Query Statistics: Enable hibernate.generate_statistics
- Connection Pool Monitoring: Track connection usage and leaks
- Cache Hit Ratios: Monitor cache effectiveness
- Slow Query Detection: Identify performance bottlenecks
Common Issues and Solutions
- LazyInitializationException: Use @Transactional or fetch joins
- OutOfMemoryError: Implement pagination and batch processing
- Connection Leaks: Proper session management and connection pooling
- Deadlocks: Optimize transaction boundaries and locking strategies
Complete Tutorial Series
Comprehensive Learning Path
This is part of a complete Hibernate tutorial series designed for senior developers and architects. Each tutorial builds upon the previous one, providing a comprehensive learning experience.
View Complete Tutorial Series View Learning RoadmapAdvanced Tutorials
Best Practices Summary
- Always use connection pooling for production applications
- Implement proper exception handling for database operations
- Use batch processing for bulk operations
- Monitor query performance and optimize slow queries
- Implement caching strategies based on data access patterns
- Use appropriate transaction boundaries to avoid long-running transactions
- Regularly update Hibernate versions for security and performance improvements